Social Determinants of Health Issue Brief
Social Determinants of Health
Medical care is a relatively small contributor to health outcomes. Social, behavioral, and physical environment factors account for 80 percent of a population’s health outcomes. Nonprofit human service agencies are critical partners in efforts to bend the nation’s health care cost curve because they address vulnerable populations’ social and behavioral factors through the provision of a wide range of services, including access to safe, stable housing; nutritious food; counseling services; recreation programs; transportation; and advocacy.
Health Care Spending
The U.S. health care crisis, which is fueled by rising costs and a high demand for medical services, affects all government and private expenditures and services. In addition, the need for often costly medical treatment is not evenly distributed among all people. “In 2015, half of the population accounted for 97% of health spending [and] the 50% of the population with the lowest spending accounted for 3% of all total health spending.”1
Discussions of cost containment often target medical and insurance providers. They ignore that the primary drivers of the need for medical services are socially and behaviorally motivated. In fact, a recent study concluded that “states with higher ratios of social to health spending had better health outcomes one and two years later.”6
Examples of Social Determinants
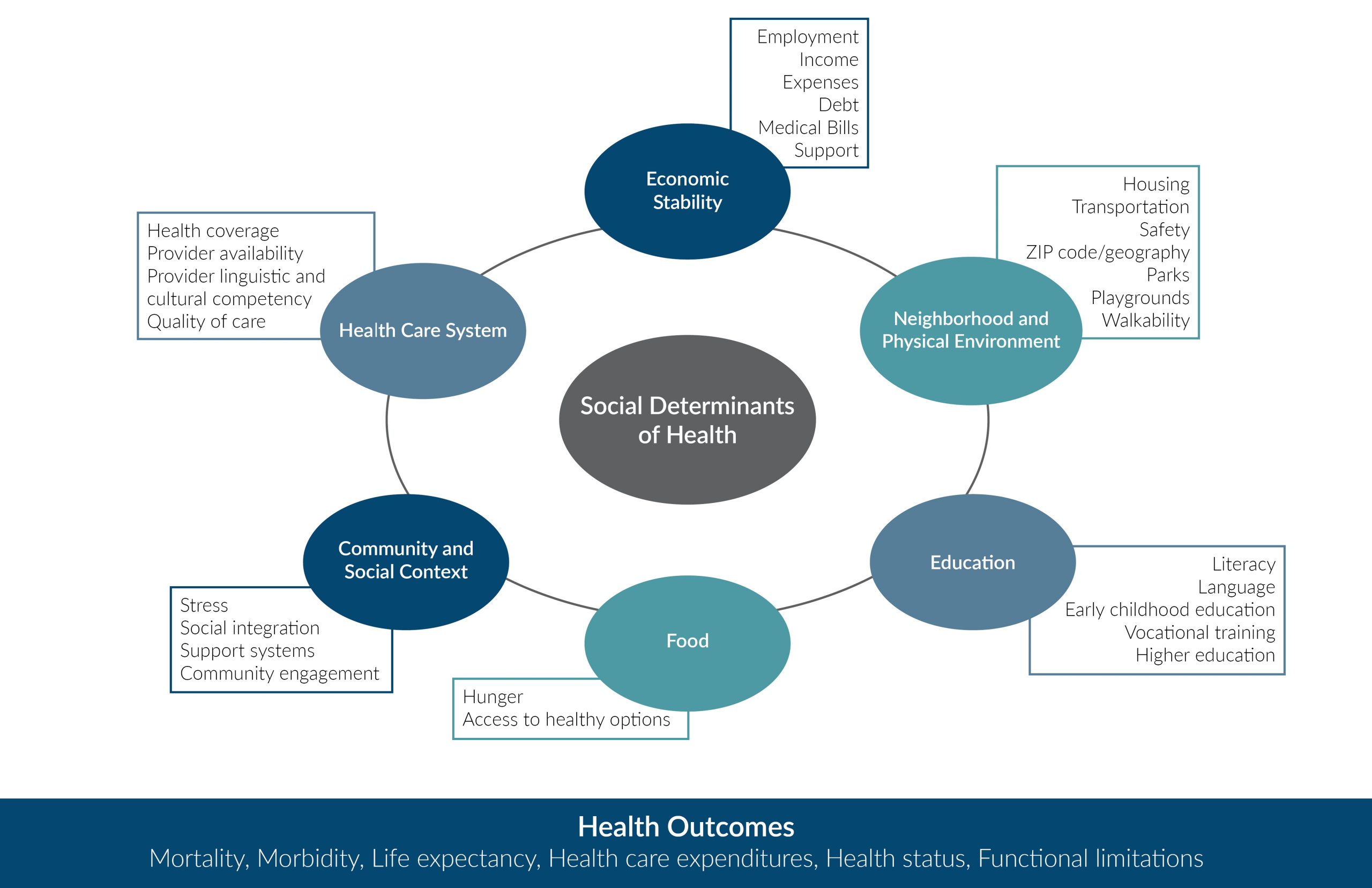
Health is shaped not only by biology, but by “where we live, labor, learn, play, and pray.”2, 3, 7 Examples of social determinants that affect health status include: Access to healthy food; Access to safe places for exercising; Access to, and the quality of, health services; Access to safe, stable housing; Environmental pollution; and Education level, including basic health literacy. The impact of multiple adverse childhood experiences has also been shown to be a strong factor in determining a person’s physical health throughout a person’s lifetime.4 Advances in neurophysiology have illuminated biological pathways between cumulative stress, brain development, and other diseases. Social and environmental determinants play a role in many chronic conditions, such as diabetes, hypertension, asthma, and heart disease.
Impact of Social Determinants
Many factors determine an individual’s health: genetic, behavioral, medical, and social. There is very strong consensus that medical care itself is a relatively small part of the picture. As depicted in the visual below, fully half of health outcomes can be explained by socio-economic factors and physical environment factors, and another 30 percent by health behaviors.3

About the Alliance for Strong Families and Communities
The Alliance is a national strategic action network driven by members aligned through shared ownership and a common vision to achieve a healthy and equitable society. We aggregate the very best sector knowledge and serve as an incubator for learning and innovation to generate new solutions to the toughest problems. We accelerate change through dynamic leadership development and collective actions to ensure policies and systems provide equal access and opportunity for: Health and well-being, Economic opportunity, Educational success, and Safety and security.

References:
- Henry J. Kaiser Foundation. (2017). How do health expenditures vary across the population? Retrieved from https://www.healthsystemtracker.org/chart-collection/health-expenditures-vary-across-population/#item-start
- Koh, H. K. (2011). The ultimate measures of health. Public Health Reports, 126(Suppl 3), 14–15. Retrieved from
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3150123/ - Alliance for Strong Families and Communities, American Public Human Services Association, Oliver Wyman, SeaChange Capital Partners, & Marsh & McLennan Companies. (2018). A national imperative: Joining forces to strengthen human services in America. Retrieved from https://www.alliance1.org/web/resources/pubs/national-imperative-joining-forces-strengthen-human-services-america.aspx
- Felitti, V. J., Anda, R. F., Nordenberg, D., et al. (1998). Relationship of childhood abuse and household dysfunction to many of the leading causes of death in adults. American Journal of Preventive Medicine, 14, 245-258. http://www.ajpmonline.org/article/S0749-3797(98)00017-8/fulltext
- Booske, B.C., Athens, J. K., Kindig, D. A., Park, H., & Remington, P.(2010). Different perspectives for assigning weights to determinants of health. Retrieved from http://www.countyhealthrankings.org/sites/default/files/differentPerspectivesForAssigningWeightsToDeterminantsOfHealth.pdf
- Bradley, E., Canavan, M., Rogan, E., Talbert-Slagle, K., Ndumele, C., et al. Variation in health outcomes: The role of spending on social services, public health, and health care, 2000–09. (2016). Health Affairs, 35, 760-768.
https://www.healthaffairs.org/doi/abs/10.1377/hlthaff.2015.0814 - Aetna Foundation & U.S. News & World Report. (2018). Healthiest communities rankings. Retrieved from
https://www.usnews.com/news/healthiest-communities/rankings
